広島大学生体システム論研究室では,長年にわり末梢動脈の血管インピーダンスに関する研究に取り組んできました.
https://bsys.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/news/17849
https://bsys.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/news/18078
https://bsys.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/news/17999
今回新たに,適切に設計された着圧ソックスによって動脈コンプライアンスが増加し脈波伝播速度(Pulse Wave Velocity, PWV)が低下することを発見し,国際学術雑誌論文として発表しました.この論文は広島国際大学,ニッティド株式会社との共同研究の成果で,D3の森永 浩介先生(広島国際大学総合リハビリテーション学部リハビリテーション支援学科,助教)の博士学位論文の一部になる予定です.この論文誌”Heliyon”はCell Pressから発行されているオープンジャーナルで,Web of Scienceの”MULTIDISCIPLINARY SCIENCES”というカテゴリーのQ1ジャーナル(Journal Impact Factorによるランキング)です.おめでとうございます!
————————————————————————-
Assessing the acute effect of compression socks on improving arterial compliance in young volunteers
Kosuke Morinaga, Masako Nakahara, Kotaro Matsura, Shigekazu Ishihara, Yasuhiro Idobata, Takafumi Kobata, and Toshio Tsuji
Heliyon, Volume 11, Issue 1, e41704, pp.1-11, doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41704, January 30, 2025. (SCIE, IF=3.4)
URL: https://www.cell.com/heliyon/fulltext/S2405-8440(25)00084-2
PDF: https://www.cell.com/action/showPdf?pii=S2405-8440%2825%2900084-2
<論文内容>
Highlights
• Wearing compression socks reduces brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity.
• Wearing compression socks is beneficial for arterial function.
• Compression socks could be important for the prevention of vascular diseases.
Abstract
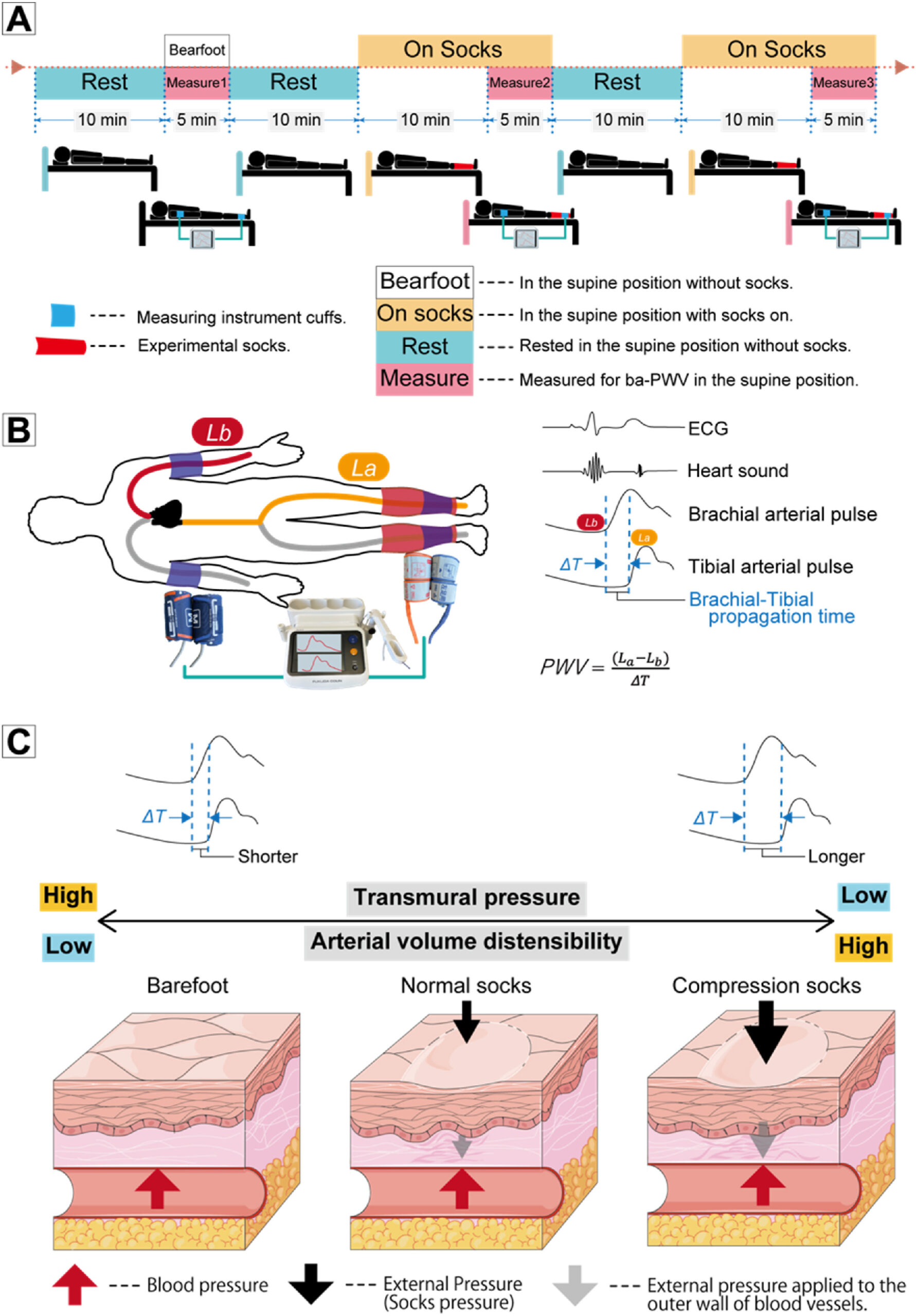
Background: Wearing compression socks increases mean deep venous velocity, reduces venous blood retention, and improves venous return. However, no existing studies reported their effect on arteries. Thus, we aimed to determine whether wearing compression socks decreases brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (ba-PWV).
Methods: We compared ba-PWV measurements in 106 participants (40 men and 66 women) under three conditions: bare feet, wearing normal socks, and wearing compression socks for 10 min. Mean arterial blood pressures (MAPs) were measured at the upper arms and ankles on both sides. Sensor cuffs were attached over socks to estimate pressures exerted on arterial walls by the socks in the condition of wearing socks.
Results: Tukey’s honestly significant difference test showed that PWVs for the compression sock26 condition were significantly lower than those for bare feet (95% confidence intervals: 0.3051–0.9478 [right], 0.3454–0.9889 [left], p<0.0001 on both sides) and normal sock conditions (0.0126–0.6552, 0.0656–0.7092, p<0.04 on both sides). The mean ba-PWV of the right side decreased from 10.57 m/s (bare feet) to 9.94 m/s (compression socks) [absolute difference: 0.63 m/s; relative difference: 5.96%]. The left-sided mean ba-PWV decreased from 10.79 m/s (bare feet) to 10.11 m/s (compression socks) [absolute difference: 0.67 m/s; relative difference: 6.21%]. We observed no significant differences in PWVs between bare feet and normal sock conditions on either side. In the compression sock condition, the difference between upper-arm and ankle MAPs while wearing socks indicates the pressure exerted on the arterial wall by the compression socks. We found significant negative correlations between ba-PWV and the estimated pressure exerted on the arterial wall at both ankles (regression analysis, F(1, 104)=10.55, p < 0.02) [right], F(1, 104)=12.92, p < 0.0005 [left]).
Conclusions: Wearing compression socks reduced ba-PWV, indicating increased arterial compliance in lower limb arteries by applying external pressure to the arterial wall.
ハイライト
– 着圧ソックスの着用は上腕-足首脈波伝播速度を減少させる.
– 着圧ソックスの着用は動脈機能に有益である.
– 着圧ソックスは血管疾患の予防に重要かもしれない.
要旨
背景 着圧ソックスの着用は平均深部静脈速度を増加させ,静脈血貯留を減少させ,静脈還流を改善する.しかし,動脈に対する効果を報告した既存の研究はない.そこで我々は,着圧ソックスの着用が上腕-足関節脈波伝播速度(ba-PWV)を低下させるかどうかを明らかにすることを目的とした.
方法:106人の参加者(男性40人,女性66人)を対象に,裸足,普通のソックス着用,着圧ソックス10分間着用の3つの条件でba-PWV測定を比較した.両側の上腕と足首で平均動脈血圧(MAP)を測定した.靴下の上からセンサーカフを装着し,靴下を履いた状態で靴下が動脈壁に及ぼす圧力を推定した.
結果:TukeyのHSD検定により,着圧ソックス条件のPWVは,裸足の条件(95%信頼区間:0.3051-0.9478[右],0.3454-0.9889[左],p<0.0001,左右とも)および通常のソックス着用の条件(0.0126-0.6552,0.0656-0.7092,p<0.04,左右とも)よりも有意に低かった.右側の平均ba-PWVは10.57m/s(裸足)から9.94m/s(着圧ソックス)に減少した[絶対差:0.63m/s、相対差:5.96%].左側平均ba-PWVは10.79m/s(裸足)から10.11m/s(着圧ソックス)に減少した[絶対差:0.67m/s,相対差:6.21%].PWVは,裸足と通常のソックス着用では左右で有意差は認められなかった.着圧ソックス条件では,ソックス着用時の上腕と足首のMAPの差は着圧ソックスが動脈壁に及ぼす圧力を示すが,Ba-PWVと両足首の動脈壁にかかる推定圧力との間に有意な負の相関が認められた(回帰分析,F(1, 104)=10.55, p<0.02)[右],F(1, 104)=12.92, p<0.0005[左]).
結論:着圧ソックスの着用はba-PWVを低下させたが,これは動脈壁に外圧を加えることによって下肢動脈のコンプライアンスが上昇したことを示している.
————————————————————————-