広島大学生体システム論研究室では,長年にわたって生体信号のモデル化と識別に関する研究に取り組んできました.最近では,古居 彬先生(広島大学大学院先進理工系科学研究科情報科学プログラム 准教授)を中心に,筋電位や脳波,心電図などの統一的なモデル化を目指してスケールミクスチャモデルを開発し,医工学分野やヒューマンインタフェースへの応用を視野に入れて研究を行っています.
今回新たに,スケールミクスチャモデルをてんかん脳波の自動識別問題に適用した論文が掲載されました.この論文は岡山大学の秋山 倫之先生(医歯薬学域准教授,診療副科長,てんかんセンター副センター長,医局長)との共同研究の成果で,古居 彬先生が博士課程前期修了生の大西 亮太君(筋電グループ)の修士研究の一部を発展させ論文化したものです.
今後も本研究チームとともに研究を継続し,臨床での研究成果につなげていければと思っています.
————————————————————————-
Epileptic seizure detection using a recurrent neural network with temporal features derived from a scale mixture EEG model
Akira Furui, Ryota Onishi, Tomoyuki Akiyama, and Toshio Tsuji
IEEE Access, Volume: 12, pp.162814-162824, Digital Object Identifier:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3487637, Date of Publication: 29 October 2024 (SCIE, IF=3.4)
URL:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10737339
PDF:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=10737339
<論文内容>
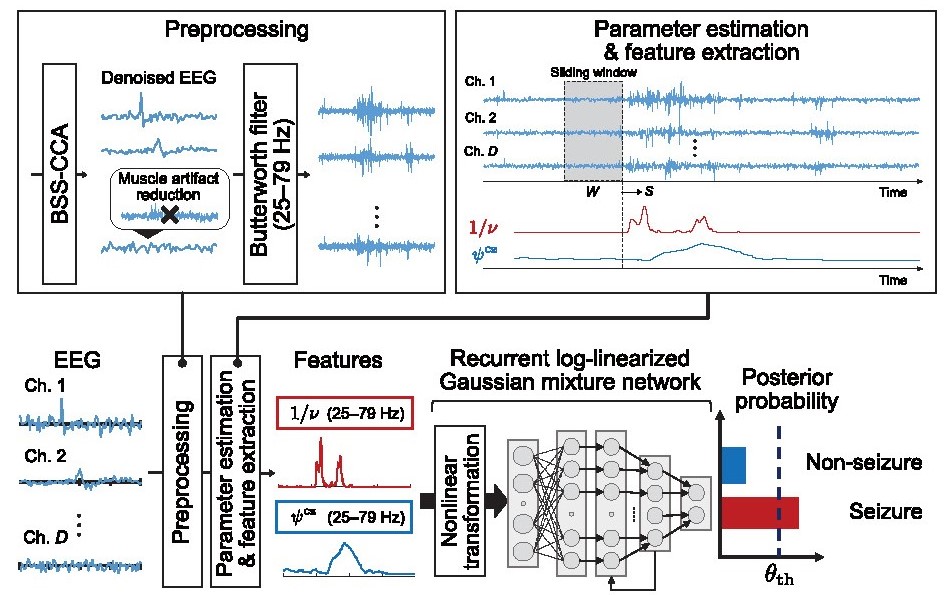
Automated detection of epileptic seizures from scalp Electroencephalogram (EEG) is crucial for improving epilepsy diagnosis and management. This paper presents an automated inter-patient epileptic seizure detection method using multichannel EEG signals. The proposed method performs both feature extraction and seizure detection based on a scale mixture-based stochastic EEG model and a recurrent neural network, respectively. Specifically, the stochastic model that can consider uncertainties in the EEG amplitude is first fitted to a specific frequency band of EEG, thereby extracting relevant features of the seizure. Then, a recurrent neural network-based recognition architecture learns the temporal evolution of these features. We evaluated our method using EEG data from 20 patients with focal epilepsy, conducting comprehensive assessments including ablation studies on classifiers and features. The results demonstrate that our approach outperforms static classifiers and existing feature sets, achieving high sensitivity while maintaining acceptable specificity. Furthermore, our feature set showed efficacy both independently and as a complement to existing features, indicating its robustness in seizure detection tasks. These findings reveal that learning the temporal evolution of the stochastic fluctuation and amplitude information of EEG extracted using a stochastic model enables highly accurate seizure detection, potentially advancing automated epilepsy diagnosis in clinical settings.
頭皮脳波(EEG)からてんかん発作を自動検出することは,てんかんの診断と管理を改善するために極めて重要である.本論文では,多チャンネル脳波信号を用いた患者間自動てんかん発作検出法を提案する.提案手法は,特徴抽出と発作検出の両方を,それぞれスケールミクスチャベースの確率的EEGモデルとリカレントニューラルネットワークに基づいて行う.具体的には,まず脳波振幅の不確実性を考慮できる確率モデルを脳波の特定の周波数帯域にフィッティングし,それによって発作に関連する特徴を抽出する,次に,リカレントニューラルネットワークに基づく認識アーキテクチャが,これらの特徴の時間的変化を学習する.我々は,局所てんかん患者20人の脳波データを用いて分類子と特徴量に関するアブレーション研究を含む包括的評価を行い,本手法を評価した.その結果,本手法は静的分類器や既存の特徴セットを凌駕し,許容可能な特異度を維持しながら高い感度を達成した.さらに,我々の特徴セットは,単独でも既存の特徴セットを補完するものとしても有効性を示し,発作検出タスクにおける頑健性を示した.これらの知見は,確率モデルを用いて抽出された脳波の確率的ゆらぎと振幅情報の時間発展を学習することにより,高精度の発作検出が可能になることを明らかにし,臨床現場におけるてんかんの自動診断を進歩させる可能性を示している.
————————————————————————-
これまでに取り組んできた脳波研究に関して掲載された研究論文は以下のとおりです.
■国際学術雑誌
A Log-Linearized Gaussian Mixture Network and Its Application to EEG Pattern Classification
T.Tsuji, O.Fukuda, H.Ichinobe and M.Kaneko
IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part C: Applications and Reviews, Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 60-72, February, 1999 (SCI, IF=0.957).
Non-Gaussianity Detection of EEG Signals Based on a Multivariate Scale Mixture Model for Diagnosis of Epileptic Seizures
Akira Furui, Ryota Onishi, Akihito Takeuchi, Tomoyuki Akiyama, and Toshio Tsuji
IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, Volume: 68, Issue: 2, pp. 515-525, Digital Object Identifier: 10.1109/TBME.2020.3006246, Publication Date: FEBRUARY 2021 (SCI, IF = 4.424)
Epileptic seizure detection using a recurrent neural network with temporal features derived from a scale mixture EEG model
Akira Furui, Ryota Onishi, Tomoyuki Akiyama, and Toshio Tsuji
IEEE Access, Volume: 12, pp.162814-162824, Digital Object Identifier:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3487637, Date of Publication: 29 October 2024 (SCIE, IF=3.4)
■国内学術雑誌
ニューラルネットによる時系列脳波パターンの識別
福田修,辻敏夫,金子真
電子情報通信学会論文誌, Vol.J80-D-II, No.7, pp.1896-1903, 1997.
次元圧縮機能を有するリカレント確率ニューラルネットの提案と時系列脳波パターン識別への応用
島 圭介,高田 大輔,卜 楠,辻 敏夫
計測自動制御学会論文集,Vol. 48,No. 4,pp. 199-206,2012.
■国際会議
Pattern Classification of EEG Signals Using a Log-Linearlized Gaussian Mixture Neural Network
O.Fukuda, T.Tsuji and M.Kaneko
Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 2479-2484, Perth, 1995.
Pattern Classification of Time-series EEG Signal Using Neural Networks
O.Fukuda, T.Tsuji and M.Kaneko
Proceedings of 5th International Workshop on Robot and Human Communication RO-MAN’96, pp. 217-222, Tsukuba, 1996.
Pattern Discrimination of Time Series EEG Signals Using a Recurrent Neural Network
Osamu Fukuda, Toshio Tsuji, Nan Bu, and Makoto Kaneko
Proceedings of the IASTED International Conference ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND SOFT COMPUTING, pp. 450-455, Banff, 2002.
EEG Discrimination using Wavelet Packet Transform and a Reduced-dimensional Recurrent Neural Network
Nan Bu, Keisuke Shima, and Toshio Tsuji
Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine (ITAB 2010), Paper-ID 261, Corfu, Greece, Nov 2-5, 2010.
A Time-Series Scale Mixture Model of EEG with a Hidden Markov Structure for Epileptic Seizure Detection
Akira Furui, Tomoyuki Akiyama, Toshio Tsuji
Proceedings of 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC’21), pp. 5832?5836, Virtual Conference due to COVID-19, Nov 1-5, 2021.
Sleep EEG Analysis Based on a Scale Mixture Model and its Application to Sleep Spindle Detection
Miyari Hatamoto, Akira Furui, Keiko Ogawa, and Toshio Tsuji
2022 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), pp. 887-892, Narvik, Norway (online), January 9-12, 2022.
Stochastic Fluctuation in EEG Evaluated via Scale Mixture Model for Decoding Emotional Valence
Shunya Fukuda, Akira Furui, Maro Machizawa, Toshio Tsuji
2024 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII 2024), pp.567-572, doi:10.1109/SII58957.2024.10417430, Ha Long, Vietnam, 8-11th January, 2024.