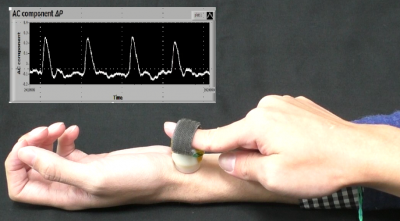
We proposed a new noninvasive and tactile measurement sensor of carotid artery pressure. The sensor unit comprises a pair of coil circuit boards, a pair of springs and a sensing plastic chip, each spring being mounted between the circuit board and the chip. The distance between the coil circuit boards is monitored from the displacement of the spring, and it is converted into a voltage signal by electromagnetic induction. First, the optimal force externally applied to the proposed sensor was investigated so that the fluctuation of the carotid pulse wave amplitude could be measured accurately. We confirmed that the force applied when the measured maximum amplitude of the sensor was obtained is the optimum force. Next, the carotid artery pulse wave was measured using these sensors with the optimal force, and compared with the carotid artery pressure measured using a commercially available pulse wave transducer. The correlation coefficient between the two carotid arteries was 0.9 or more. We concluded that the proposed sensor enables noninvasive measurement of the carotid pulse wave.
Resarch topics
Sphygmomanometer using Electromagnetic Induction
References
1.Development of a Palpable Carotid Pulse Pressure Sensor Using Electromagnetic Induction (in Japanese), Harutoyo Hirano, Tomohiro Fukuchi, Yuichi Kurita, Akihiko Kandori, Yuko Sano, Ryuji Nakamura, Noboru Saeki, Masashi Kawamoto, Masao Yoshizumi, and Toshio Tsuji, IEEJ Transactions on Electronics, Information and Systems, Vol. 132, No.12, pp. 1934-1942, 2012.
2.Development of a Palpable Carotid Pulse Pressure Sensor Using Electromagnetic Induction, Harutoyo Hirano, Tomohiro Fukuchi, Yuichi Kurita, Akihiko Kandori, Yuko Sano, Ryuji Nakamura, Noboru Saeki, Masashi Kawamoto, Masao Yoshizumi, Toshio Tsuji, 2012 IEEE/ICME International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering (CME 2012), pp. 441-444, Kobe, Japan, July 1-4, 2012.